Electric Cars and Battery Recycling: Understanding their Environmental Footprint
As we confront the consequences of climate change and strive to decrease our dependence on fossil fuels, electric cars have emerged as a viable solution. Unlike traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, electric cars do not produce harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, or particulate matter, making them an appealing option for environmentally conscious individuals.
However, concerns have been raised regarding the environmental impact of electric cars, specifically concerning battery production and disposal. The production of batteries necessitates the mining and processing of rare minerals, which may have negative environmental consequences.
Furthermore, electric car batteries have a limited lifespan, and once they degrade to the point where they can no longer hold a charge or function effectively, their disposal becomes problematic. In this article, we will investigate the environmental impact of electric cars, the challenges associated with battery disposal, and possible solutions for reducing their impact.
The challenge of Battery disposal: recycling and repurposing as solutions
Firstly, it is important to note that while electric cars do not emit harmful pollutants, they do contribute to carbon emissions through the production and transportation of the electricity used to power them. Nevertheless, the overall lifecycle emissions of electric cars are significantly lower than those of gasoline-powered cars, even when considering the emissions generated during electricity generation.
Moreover, while the production of batteries for electric cars may have some negative environmental impact, research has demonstrated that the overall emissions of electric cars are still significantly lower than those of gasoline cars. A study published in the journal Nature Sustainability revealed that electric cars produced half the emissions of gasoline cars over their lifetime, even when accounting for the environmental impact of battery production.
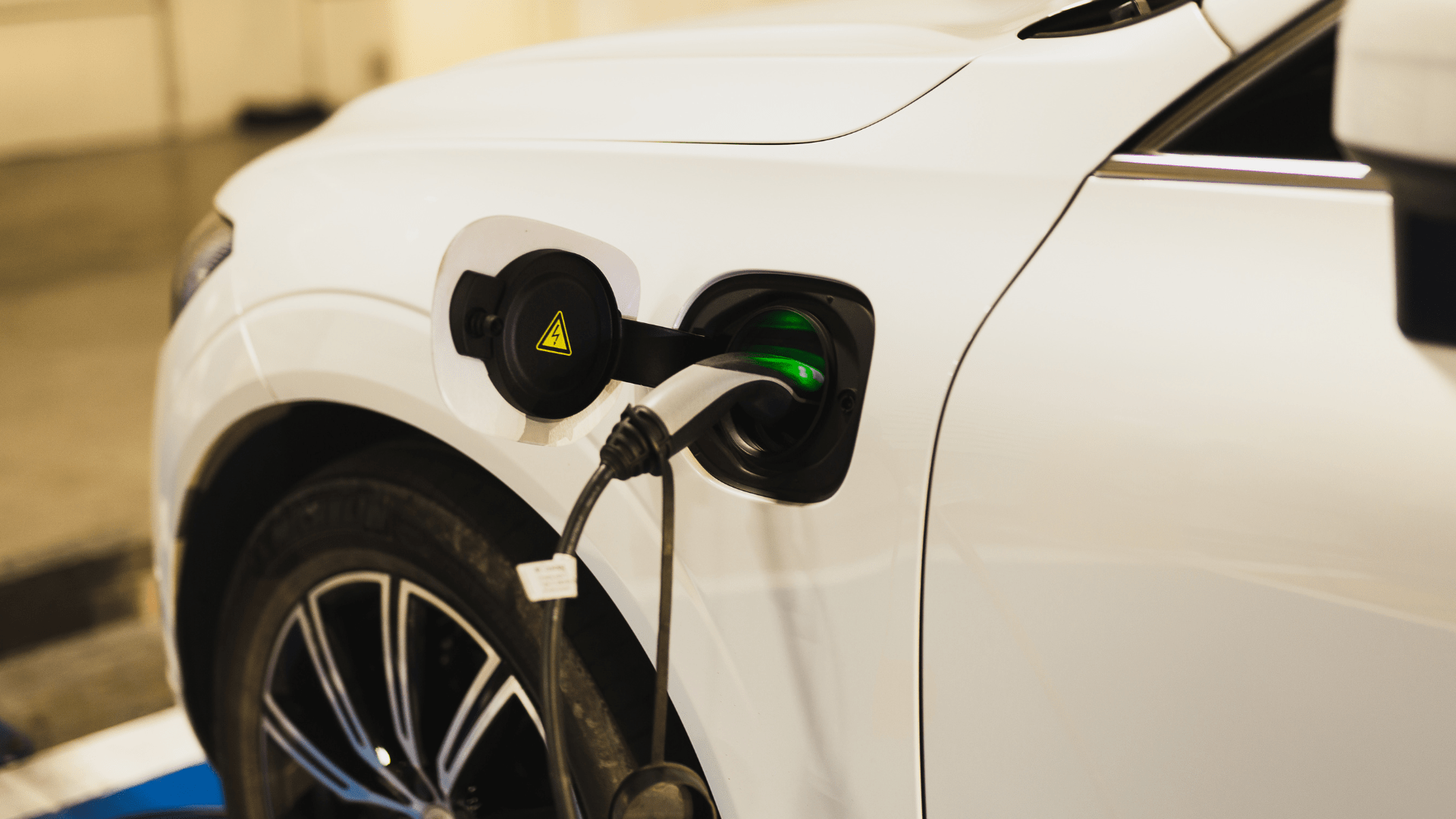
Nonetheless, battery disposal remains a significant challenge because electric car batteries contain valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These materials can be reused through recycling, which involves extracting them from the battery and using them to create new batteries or other products. However, the battery recycling process can be complex and expensive, and there is currently insufficient infrastructure in place to recycle all the batteries that will eventually need to be disposed of.
Another solution is repurposing electric car batteries for other applications, such as storing renewable energy from solar panels or wind turbines. This can extend the battery’s lifespan and reduce the need for new batteries to be produced.
However, if recycling or repurposing is not feasible, proper disposal of electric car batteries is necessary. Some of the materials used in electric car batteries, such as lithium and cobalt, can be toxic and harmful to the environment if not handled appropriately.
In conclusion, electric cars offer a promising solution for reducing emissions and combating climate change. Although the production and disposal of electric car batteries pose challenges, solutions like recycling and repurposing are being explored to mitigate their impact. We must continue to investigate and invest in sustainable solutions to ensure a cleaner and more sustainable future for all.